For those involved in the medical waste treatment industry, you might be wondering if there is a best solution for handling medical waste. Let's start by understanding what medical waste is and how we can manage it effectively.
Medical waste can consist of a variety of materials, including rubber, glass, plastics, textiles, gauze, needles, scalpels, and more. The density of these materials ranges from 65 to 3600 kg/m³. So, what should we do with the waste collected from hospitals, clinics, laboratories, and other medical facilities? Clearly, we cannot treat medical waste the same way we handle general solid waste. At the very least, we cannot send it directly to landfills, as it is classified as hazardous waste.
In fact, as time has passed, direct landfill disposal of medical waste has been increasingly restricted in many countries and regions. Companies like GEP ECOTECH have emerged, offering solutions for stale waste recycling. However, today we are focusing on more commonly accepted methods for managing medical waste.
While landfill disposal is still permitted in some areas, it must be done according to strict local laws and regulations. From a technical perspective, medical waste must undergo high-temperature disinfection, essentially a decontamination process. Autoclaving is often a crucial first step in this process. To reduce landfill space usage, many service providers also carry out volume reduction, a step that is gaining widespread acceptance, particularly in regions like the Gulf Area and other economically stable areas. At this stage, a robust, durable shredder and a stable autoclave are essential equipment investments. GEP ECOTECH is gaining recognition in the market due to its extensive disposal experience and excellent project service capabilities.
If you're from regions in Africa or Southeast Asia, such as the Philippines, you might consider incineration as a feasible solution. However, as I've emphasized, local regulations must be strictly adhered to, especially when it comes to managing flue gases from incinerators. In some cases, traditional methods may still be necessary.
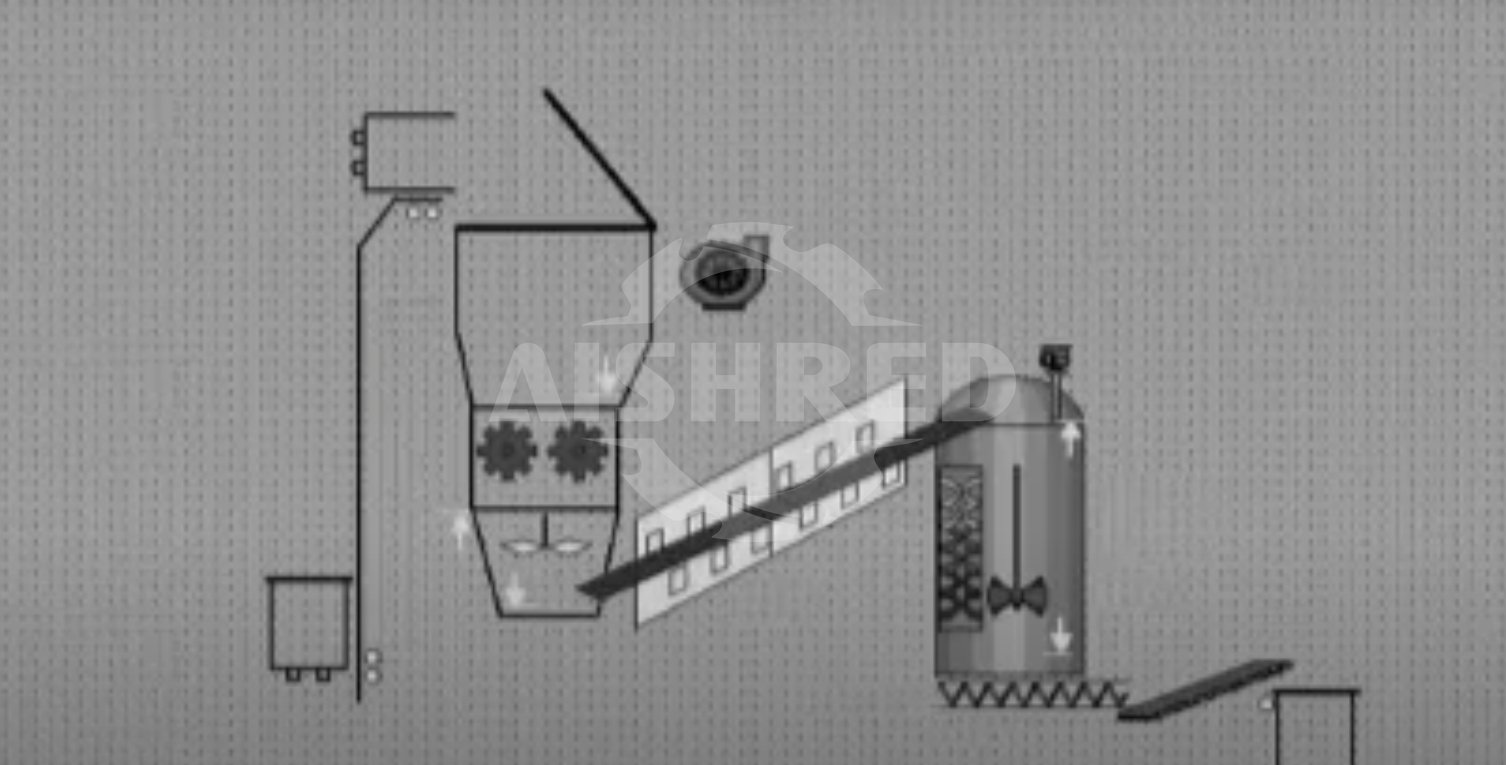
In recent years, especially in Europe and economically developed regions, there has been a strong trend toward harmless disposal and even resource recovery of medical waste. This means that after a safe and high-standard disposal process, medical waste can be treated as general solid waste or even converted into domestic waste. A key first step in this process is often safe and efficient pre-shredding, which may require specialized materials like 316 stainless steel or systems designed for cleaning and disinfection to match the subsequent harmless disposal processes. Medical sterilizers, which process waste at high pressure and temperature, have become an indispensable part of the equipment. After treatment, the material is not only sterile but also almost unrecognizable. The downside of this approach is that the upfront investment and purchasing costs can be prohibitive for some investors. However, based on projects GEP ECOTECH has participated in, this type of investment is often favored by government agencies, large enterprises, or investors.

Returning to the original question, in my view, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. People tend to make investment choices based on what is most beneficial in the moment. Since its inception, GEP ECOTECH, a company specializing in the development of solid waste disposal equipment, has focused on providing customized solutions to meet the unique needs of our customers.
Feel free to give us a call or send us a message, and let's discuss how we can help solve your specific waste treatment challenges!

