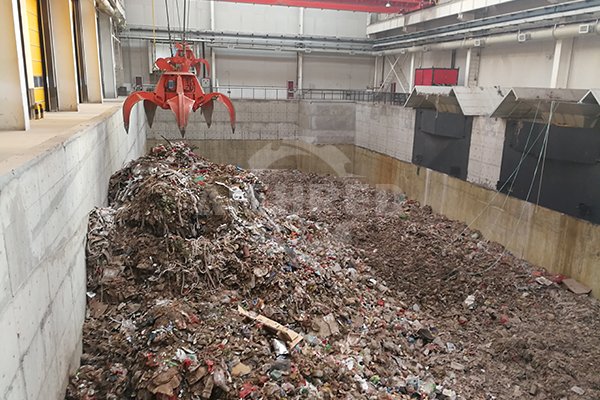
Municipal solid waste management is a crucial challenge facing modern cities today. With the rapid pace of urbanization and population growth, the volume of waste generated continues to increase, posing significant challenges to the environment and public health. These municipal wastes stem from households, businesses, and institutions, encompassing various solid wastes such as paper, plastic, glass, and food residues. Effectively handling and managing these wastes is paramount, requiring systematic solutions to ensure environmental protection, resource recovery, and public health.
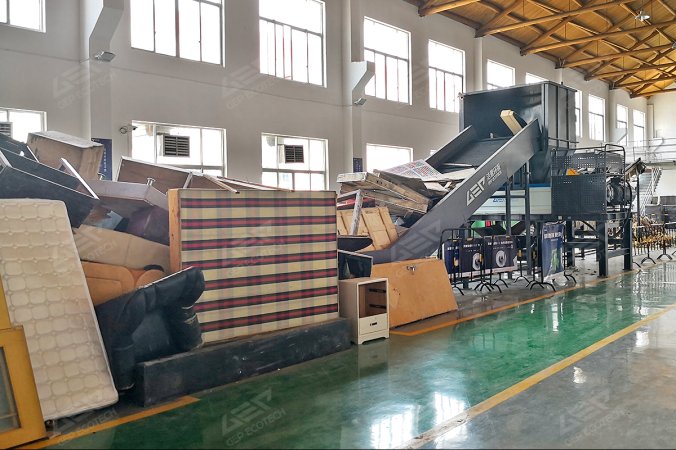
One of the challenges in urban solid waste management is the sorting of mixed wastes. Despite the implementation of waste sorting in some developed regions for many years, many cities still grapple with mixed waste, making efficient sorting a crucial challenge.
Regarding waste treatment, modern cities employ various technologies and methods, including recycling, incineration, landfilling, and organic waste treatment.
GEP ECOTECH has developed diverse solutions tailored to the characteristics of different municipal solid wastes in cities. We prioritize reducing manual operations on production lines to enhance efficiency and diminish the impact of harsh environments on workers. Simultaneously, we are committed to advancing the application of innovative technologies, offering more comprehensive and efficient solutions in the field of waste management.
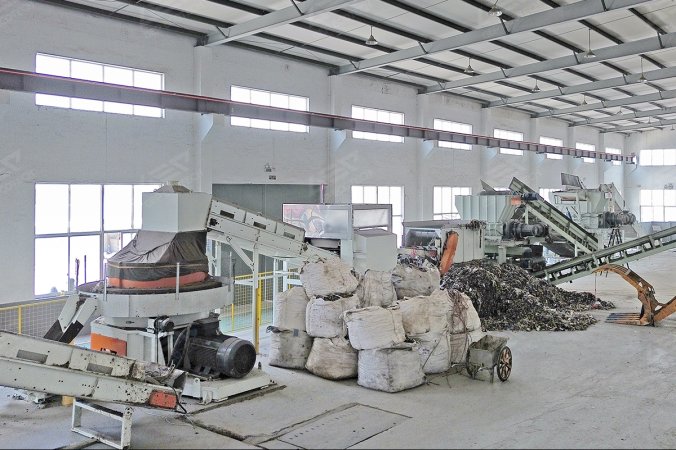
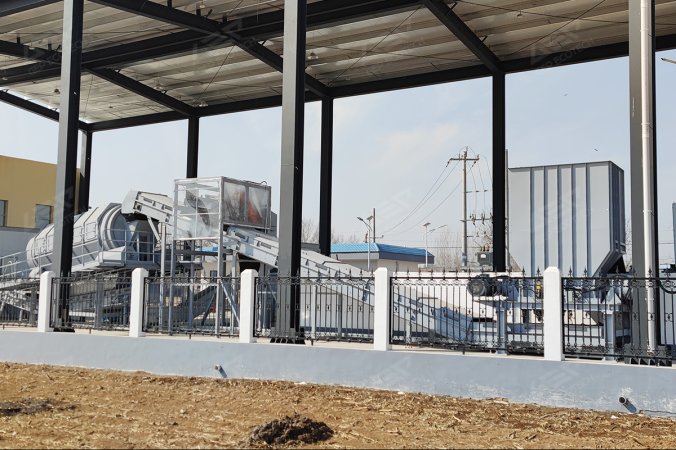
Sorting and Recycling
The significance of sorting and recycling urban solid waste lies in minimizing landfill waste, reducing resource wastage, and enhancing the recyclability of materials. This process involves utilizing advanced technologies and equipment to effectively separate and categorize various types of waste.
Sorting typically involves a variety of methods including automated equipment, sensors, and manual sorting based on the materials. It separates recyclables such as paper, plastic, metal, and glass from the waste stream for further processing and reuse. Simultaneously, organic waste is segregated for purposes like biomass energy or composting, reducing the landfilling of organic materials.
Incineration or Alternative Fuel
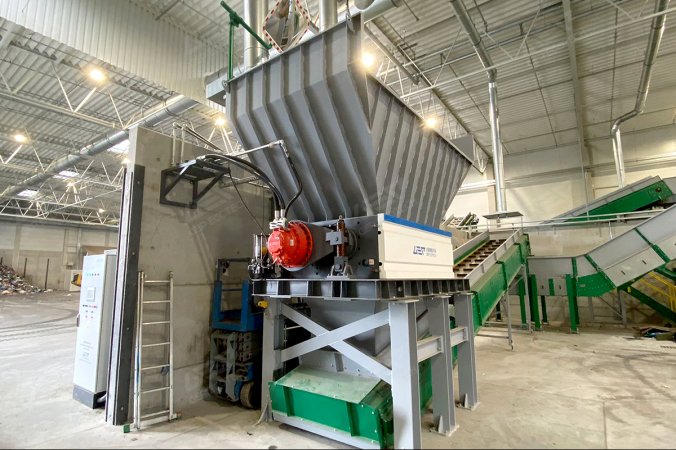
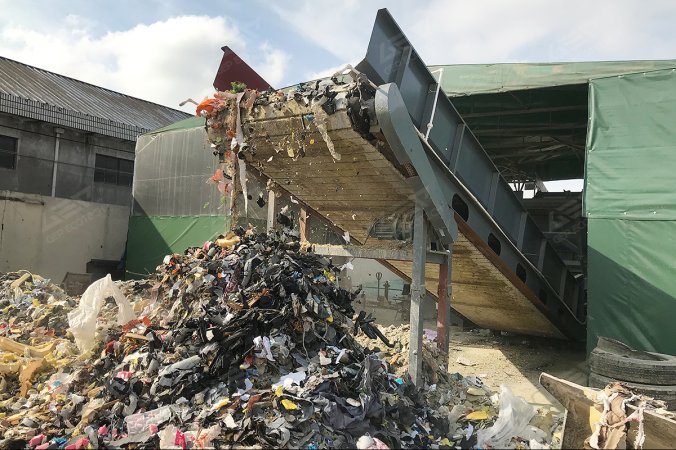
Converting combustible components from urban solid waste into energy through incineration or as an alternative fuel in boilers is an eco-friendly and cost-effective method. The process involves the consistent separation of recyclables like metals, glass, food residues, and inert materials from the waste. Then, the combustible materials are processed into suitable sizes for incineration and, if necessary, converted into pellets (known as RDF).
The primary challenge in this process is controlling moisture content. For wet waste, we recommend biological processing to reduce moisture before handling.
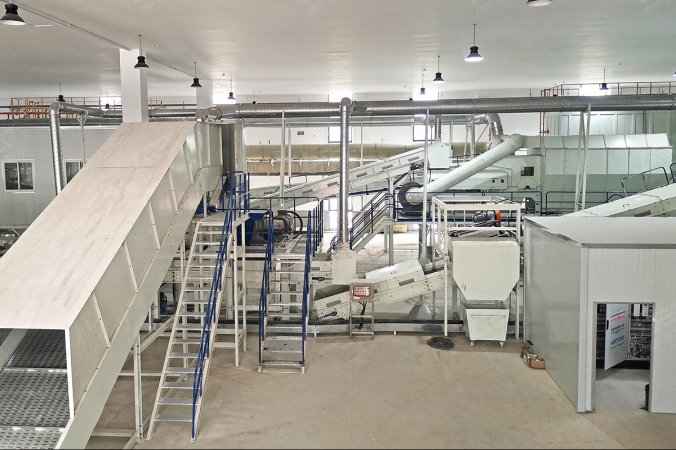
Mechanical Biological Treatment
Mechanical biological treatment (MBT) is a popular waste management option for urban solid waste, especially for waste with a high organic content. It combines mechanical processes (separation and recovery) with biological processes (composting or fermentation). MBT relies on minimal infrastructure and equipment, offering an economically efficient waste management solution.
However, MBT has drawbacks, including lower compost quality and a risk of soil contamination. It's seen as a transitional solution towards achieving zero waste.
Landfill Mining
Landfill Mining involves recovering materials from filled or inactive landfill sites. The process aims to extract valuable resources, like metals and plastics, which were discarded and buried. It helps reduce environmental risks and retrieve materials for reuse.