
cement plant, power plant, paper mill, transportation industry.




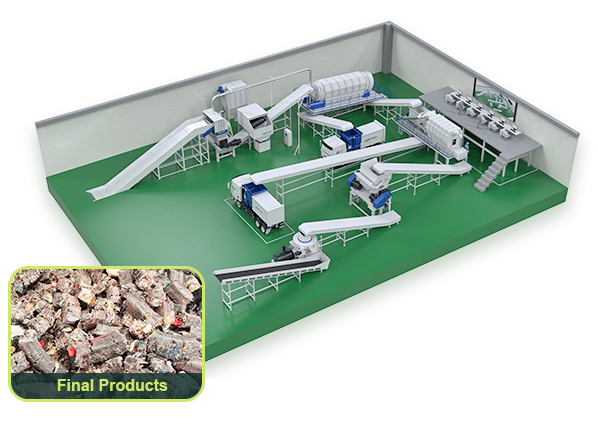
RDF refers to solid fuel made of combustible parts selected from MSW and treated through processes such as shredding, sorting, and pelletizing. It has the characteristics of high calorific value, stable combustion, easy transportation, easy storage, low secondary pollution, and low emissions of dioxins.
Organic waste, paper, plastic and other combustible substances in MSW.
By shredding and sorting MSW, non combustible materials such as metals, glass, sand, are removed from the waste. Combustible materials (such as plastics, fibers, rubber, wood, paper) in the waste are further shredded and compressed into pellets, and finally made into solid fuel.
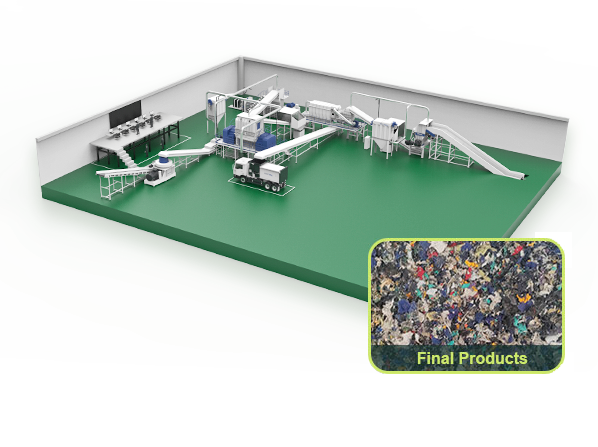


SRF is a solid fuel prepared from solid waste sources other than hazardous waste, and is classified and regulated according to ISO standards. The significant difference between SRF and RDF is that SRF has been standardized and production needs to comply with the standards set by regulatory agencies.
Non-household waste, mainly commercial, industrial, and construction waste.
The preparation process of SRF includes multiple steps such as multi-stage shredding, fine sorting, deep purification, efficient drying, and dense pelletizing. Internationally, SRF can be traded in the form of rods, columns, granules, or flocs.
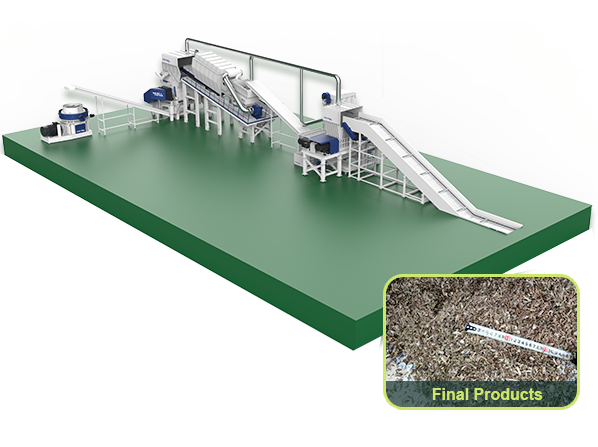
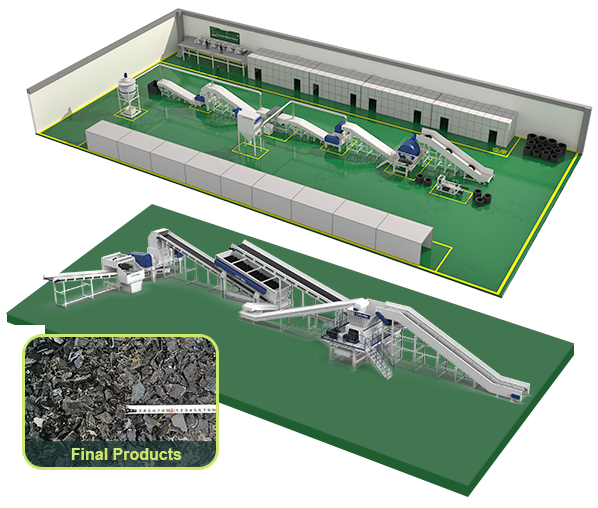
TDF is a solid fuel made by processing waste tires through shredding, screening, cutting, and other processes. Its core value lies in its high calorific value characteristics (comparable to petroleum, 25%-50% higher than coal), while reducing waste accumulation and carbon emissions.
Various waste tires (from cars, trucks, construction machinery, agricultural machinery, rubber products)
Waste tires are shredded by tire shredders or integrated slicing and dicing machines, and then transported to the cement kiln rear decomposition furnace for combustion according to a fixed ratio, achieving the substitution of fossil fuels.

Biomass pellet fuel is a high-density granular or block fuel made from agricultural and forestry waste such as straw, sawdust, rice husks, and tree branches through processes such as shredding, drying, and extrusion. It has the characteristics of high calorific value, easy storage, stable combustion, and low pollution.
Agricultural waste (straw, peanut shells, rice husks, etc.), forestry waste (woodchips, barks, sawdust, etc.), industrial organic waste (furfural residue, edible mushroom residue, bagasse, etc.), urban greening waste, and discarded furniture (non-pollution wooden parts).
Through two-stage shredding using biomass shredder and biomass fine shredder, as well as sorting and impurity removal using magnetic separator and sorting system, the raw materials are finally compressed into solid pellets using a pellet mill.

 Biomass Boiler Fuel Preparation Project in the Philippines
Biomass Boiler Fuel Preparation Project in the Philippines
 Tire Alternative Fuel Project in Macao, China
Tire Alternative Fuel Project in Macao, China
 Paper Mill Waste Alternative Fuel Project in South Korea
Paper Mill Waste Alternative Fuel Project in South Korea
 Scrap Leather RDF Project in Zhejiang, China
Scrap Leather RDF Project in Zhejiang, China
 MSW to RDF Project in HangZhou, China
MSW to RDF Project in HangZhou, China
 Mixed Plastic Alternative Fuel Project in Romania
Mixed Plastic Alternative Fuel Project in Romania
 Domestic Waste SRF project in Shanghai
Domestic Waste SRF project in Shanghai
 Garden Waste and Fabric Waste RDF Project in Jiangxi, China
Garden Waste and Fabric Waste RDF Project in Jiangxi, China
 Waste Textile to RDF Project in Zhejiang, China
Waste Textile to RDF Project in Zhejiang, China
 Straw Biomass Fuel preparation Project in Northeast China
Straw Biomass Fuel preparation Project in Northeast China